Model 106
Midsize, cylindrical ADR cryostat
Midsize, cylindrical ADR cryostat
Looking for customer support? Ready to learn more about our products and services?
Contact Sales TodayReceive product updates and event notifications
Subscribe to Our Newsletter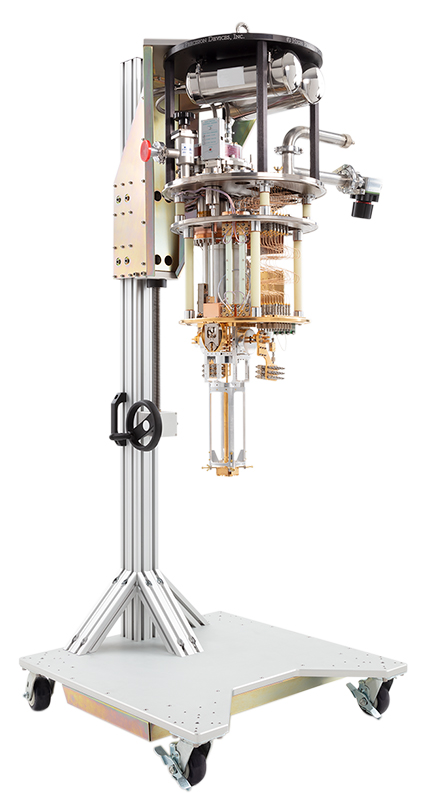

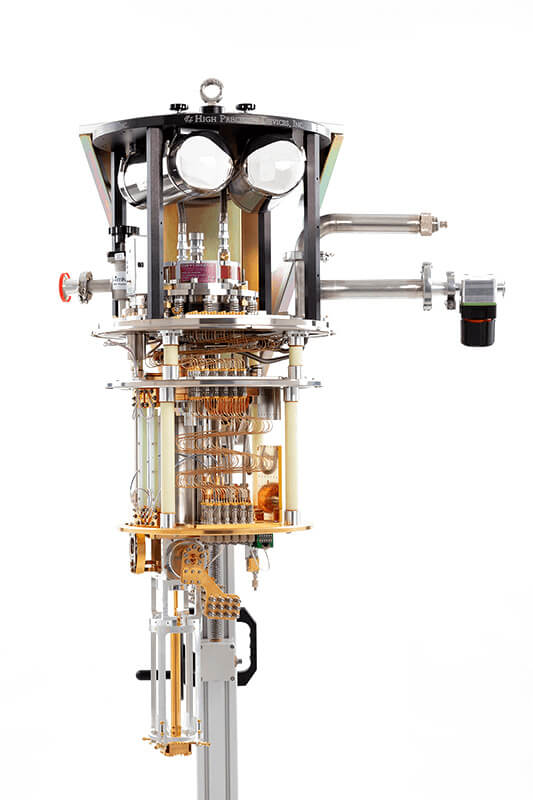
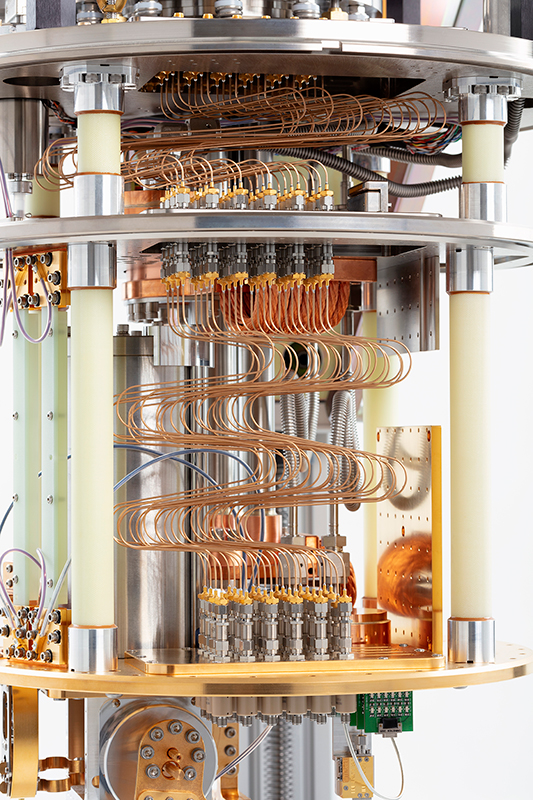
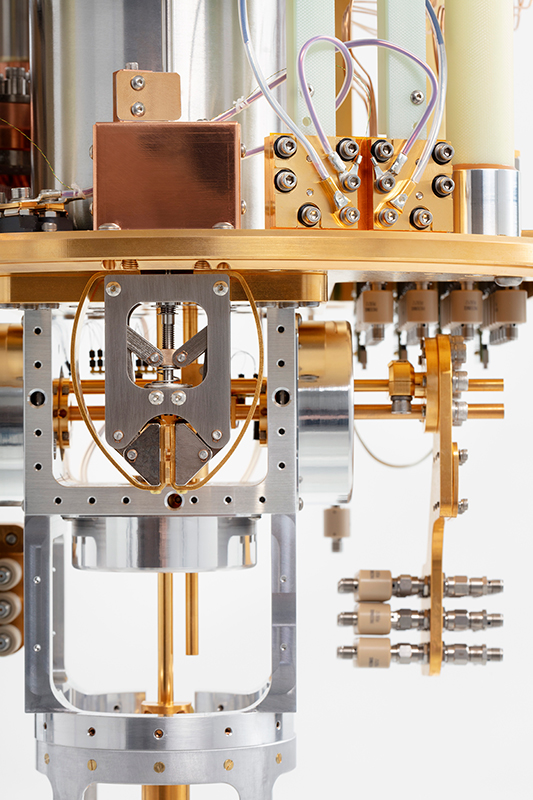
The Model 106 adiabatic demagnetization refrigerator (ADR) cryostat has been optimized for flexibility and versatility. It aims to support ultra-low temperature research by providing quick and affordable access to mK temperatures. Many customizable options make it easy to reconfigure to fit your needs.
This system uses a two stage ADR to reach temperatures as low as 30 mK. An ADR operates by submitting a salt crystal to strong magnetic fields. In these different states, the salt crystal will either absorb or dump thermal energy. This is used to shuttle heat away from the sample stage achieving mK temperatures. Because of the nature of this process, only a certain amount of heat can be absorbed before the crystal must be warmed up and regenerated.
Designed with customization in mind, the Model 106 is fitted with two large electrical bread boards at both 4 K and 50 K. Additionally, there are multiple customizable feedthroughs in each stage plate. If you are constrained by cooldown times, the Model 106 can support Rapid Cool liquid nitrogen heat exchangers. It is a robust “turn-key” mK alternative to dilution refrigerators.
Applications: Astronomy, Spin QC, Photonic QC, Material Characterization, Condensed Matter Physics
Cryogenic Tools for Quantum Development
This Keysight University course is intended to introduce researchers and scientists to the basics of cryostats, and cryogenic probe systems that are used in quantum development programs. Users will learn about the components of a cryostat, state-of-the-art methods for loading a device in a milli-Kelvin cryostat for pre-characterization of qubits, and the functionality of cryogenic probing systems for characterizing devices at temperatures below 4K.
Receive product updates and event notifications
Subscribe to Our Newsletter